Mapping my trip with GMT and Inkscape
08 Dec 2016 Philipp Boersch-Supan GIS code Tweet this!This morning I tweeted some maps of my upcoming trip to sub-antarctic New Zealand. Here is how I made them.
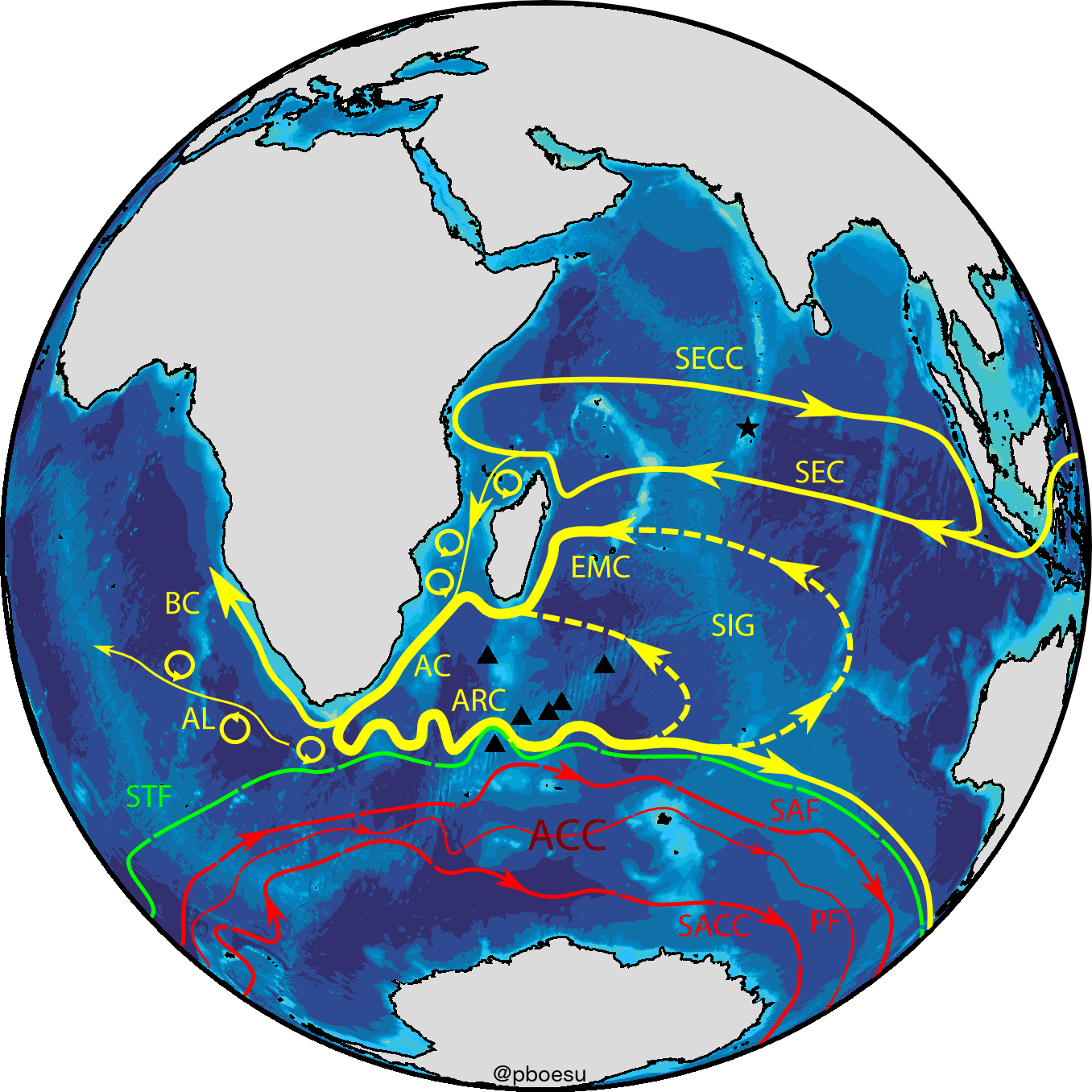
For most of my dealings with spatial data I use either R (with it’s great ecosystem of ), or a full-fledged GIS package such as GRASS or QGIS (if I need a more interactive work environment and/or particular geoinformatics tools). This combination covers pretty much all the bases for my spatial analysis and mapping needs. However, occasionally I want to make a pretty map that isn’t rectangular (usually world maps, or maps of large sections of the world) and/or one that is projected in a certain way. Maybe something like this figure of the circulation in the Southern Indian Ocean I made for my PhD thesis:
Making “publication quality” maps in all kinds of projections is a real strength of the Generic Mapping Tools aka GMT, a software suite that is popular with marine geologists and is firmly grounded in the unix paradigm of one tool - one command line utility. As such the syntax and the mapping workflow may seem like a blast from the past for many (cool kids use D3 for fancy maps these days, but apparently I’m not one of them) - but with a moderate amount of pain one can get beautiful maps that put your old Mercator or unprojected WGS84 rectangles to shame.
GMT natively writes all output to postscript files, which makes the resulting maps editable in vector graphics software such as Inkscape. This is great for tweaking or polishing graphics that go beyond maps of spatial data. In the above figure of ocean currents, for example, I used GMT to plot the globe and the bathymetry (subsea topography), but the stylized fronts and currents were added in Inkscape (based on projected coordinates of frontal locations plotted with GMT in an intermediate step).
I did something similar, but much simpler, for the maps I tweeted today, and I’ll show the individual steps below.
Step 1: Draw the map
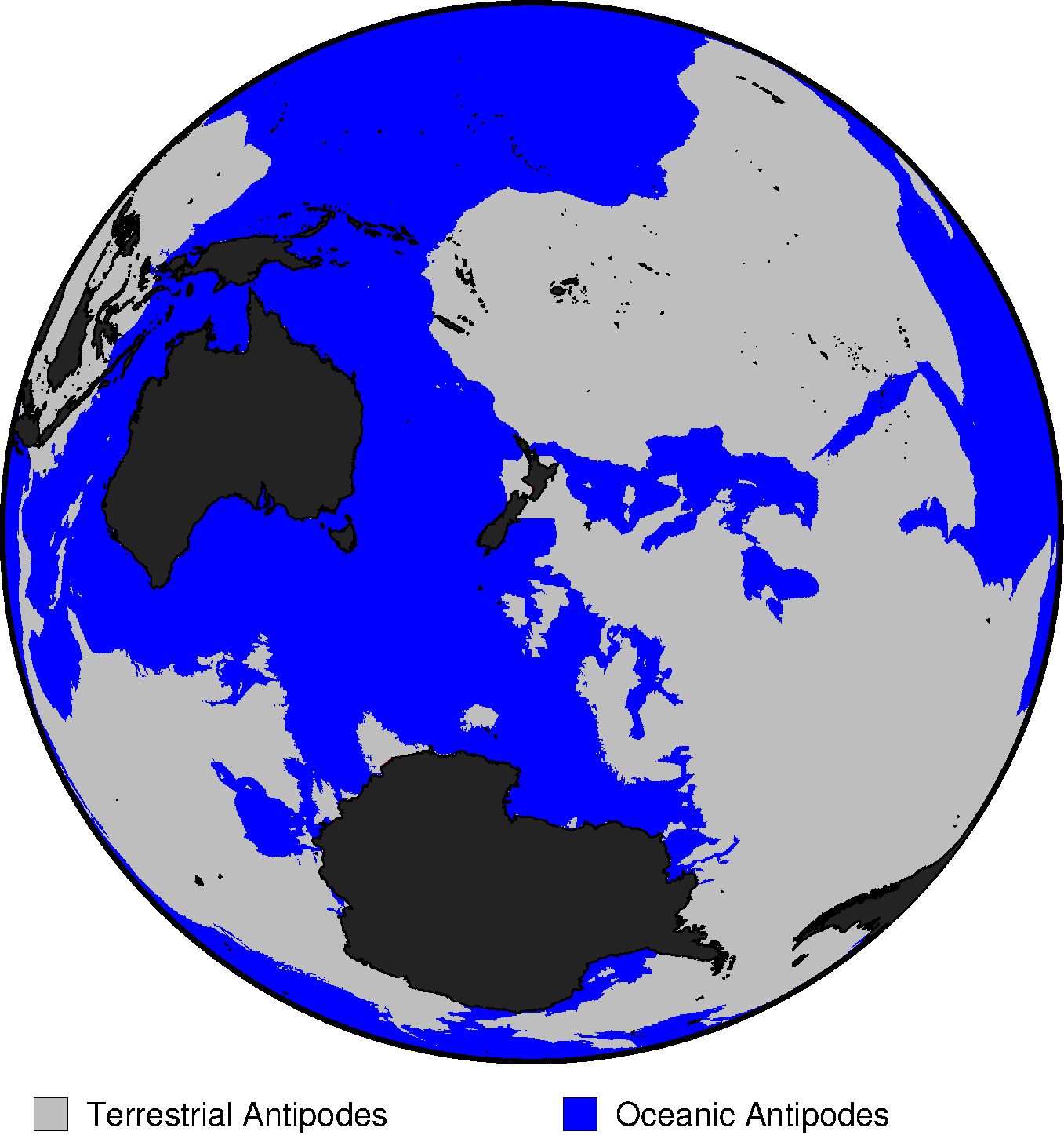
I adapted one of the GMT examples to show what’s on the opposite side of the world during my trip. The code for this is given below, and also in the script antipodes.sh on github.
This time I was happy with the GMT output as is, so no post-GMT modifications.
#!/bin/bash
# This map is a quick and dirty adaptation of GMT EXAMPLE 25
# (using GMT 5.4.0_r17345)
#
# Purpose: Display distribution of antipode types around NZ
# GMT modules: gmtset, grdlandmask, grdmath, grd2xyz, gmtmath, grdimage, pscoast, pslegend
# Unix progs: cat
#
# Create D minutes global grid with -1 over oceans and +1 over land
D=10
gmt grdlandmask -Rg -I${D}m -Dc -A500 -N-1/1/1/1/1 -r -Gwetdry.nc
# Manipulate so -1 means ocean/ocean antipode, +1 = land/land, and 0 elsewhere
gmt grdmath -fg wetdry.nc DUP 180 ROTX FLIPUD ADD 2 DIV = key.nc
# Calculate percentage area of each type of antipode match.
gmt grdmath -Rg -I${D}m -r Y COSD 60 $D DIV 360 MUL DUP MUL PI DIV DIV 100 MUL = scale.nc
gmt grdmath -fg key.nc -1 EQ 0 NAN scale.nc MUL = tmp.nc
gmt grd2xyz tmp.nc -s -ZTLf > key.b
ocean=`gmt math -bi1f -Ca -S key.b SUM UPPER RINT =`
gmt grdmath -fg key.nc 1 EQ 0 NAN scale.nc MUL = tmp.nc
gmt grd2xyz tmp.nc -s -ZTLf > key.b
land=`gmt math -bi1f -Ca -S key.b SUM UPPER RINT =`
gmt grdmath -fg key.nc 0 EQ 0 NAN scale.nc MUL = tmp.nc
gmt grd2xyz tmp.nc -s -ZTLf > key.b
mixed=`gmt math -bi1f -Ca -S key.b SUM UPPER RINT =`
# Generate corresponding color table
gmt makecpt -Cblue,gray,red -T-1.5/1.5/1 -N > key.cpt
# Create the final plot and overlay coastlines
gmt set FONT_ANNOT_PRIMARY +10p FORMAT_GEO_MAP dddF
range="g"
proj="G-185/-45/4.5i"
psfile='enderby_antipodes.ps'
#plot antipodes raster
gmt grdimage key.nc -R${range} -J${proj} -Ckey.cpt -B10/10 -P -K > $psfile
#overplot landcover
gmt pscoast -R${range} -J${proj} -Dl -A0/0/1 -G35 -W0.4p -O -K >> $psfile
#add legend
gmt pslegend -R${range} -J${proj} -O -DJBC+w4.5i -Y-0.75i >> $psfile << END
N 2
S 0.15i s 0.2i gray 0.25p 0.3i Terrestrial Antipodes
S 0.15i s 0.2i blue 0.25p 0.3i Oceanic Antipodes
END
#convert to PNG
gmt psconvert -Tg -A $psfile
#remove intermediate results
rm -f wetdry.nc scale.nc key.nc tmp.nc key.cpt key.b gmt.conf